Keywords
Abstract
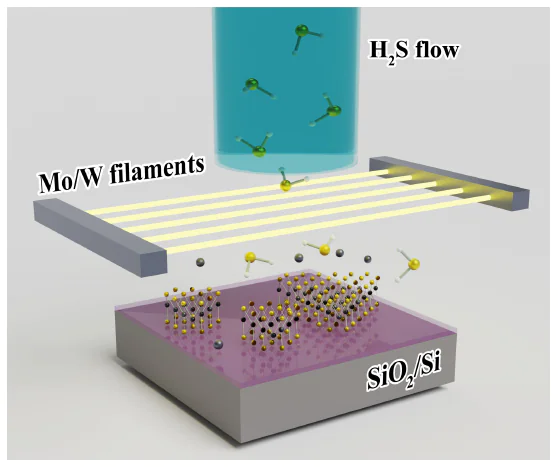
Transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) are attracting continuously growing attention due to a number of their unique properties. Possibilities of their application are significantly defined by improvement of obtaining methods. In this work we study formation of TMD (MoS2, WS2) mesoporous films during chemical vapor deposition with the use of gaseous H2S and thermally evaporated transition metals (Mo or W). Morphology, Raman spectra, photoluminescent properties and electrical conductivity of TMD films are investigated at different precursors concentrations and deposition duration times. The analysis revealed main stages of TMD films growth: isolated 2D monocrystalline islands formation (i), partial overlapping of these crystallites with their gradual growth in the plane of the substrate (ii), formation and growth of plate-like crystallites oriented perpendicular to the substrate surface (iv). Qualitative changes of morphology, electrical conductivity and PL properties of TMD films are explained with taking into account interaction of TMD electronic sub-system with the substrate and neighboring crystallites.